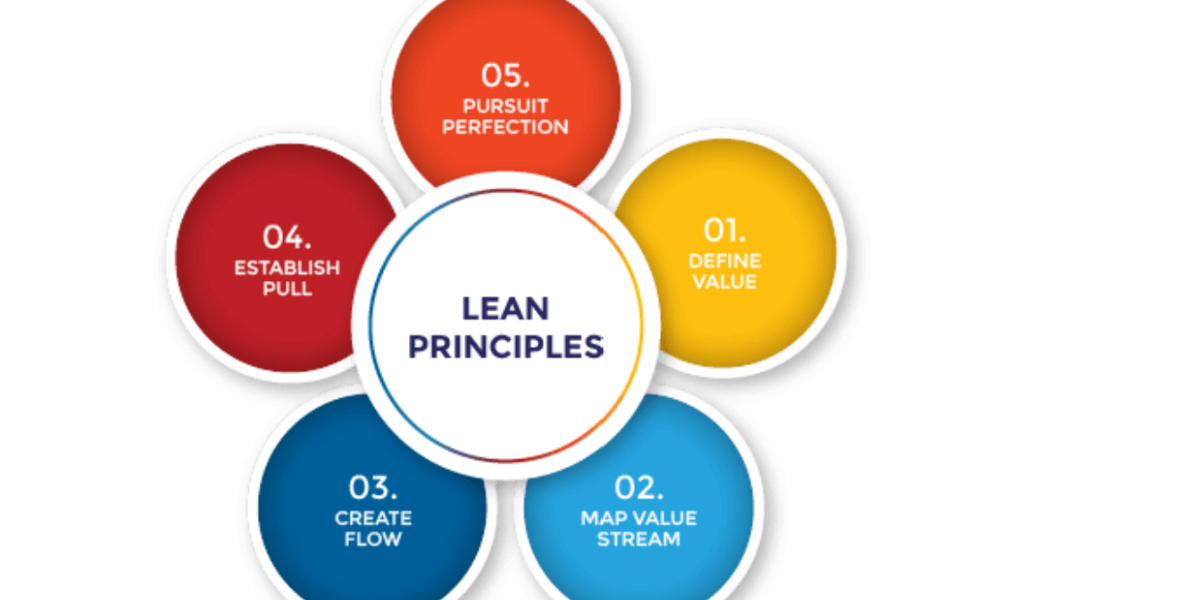
some key principles of the Lean framework
The Lean framework is a methodology for process improvement that emphasizes eliminating waste, continuous improvement, and customer value. Some key principles of the Lean framework include
- Define Value: Identify the value stream and define value from the customer’s perspective.
- Map the Value Stream: Identify all steps in the value stream and map them to identify waste and areas for improvement.
- Create a Future State Value Stream: Design a future state value stream that is ideal and achievable, and that will deliver value to the customer.
- Reduce Waste: Identify and eliminate waste in the value stream, focusing on the eight types of waste: overproduction, waiting, transportation, inventory, motion, excess processing, rejects, and skills.
- Implement the Future State: Implement the future state value stream, using techniques such as rapid improvement events, continuous improvement teams, and visual management.
- Continuously Improve: Continuously improve the value stream by identifying and addressing opportunities for improvement, and by implementing changes that will deliver value to the customer.
- Respect for People: Respect for people is a fundamental principle of Lean, and it means that employees are valued and respected as individuals and team members.
- Focus on Process: Lean emphasizes the importance of focusing on process, rather than people, as the primary means of improving efficiency and effectiveness.
- Continuous Flow: Lean aims to create a continuous flow of value delivery, by eliminating batching and reducing variability.
- Pull Production: Lean uses a pull production system, where production is based on customer demand, rather than pushing production through the system regardless of demand.
- Perfection: Lean strives for perfection, by continuously improving processes and eliminating waste.
- Visual Management: Lean uses visual management techniques, such as visual boards and metrics, to provide visibility into the process and to help identify opportunities for improvement.
- Empowerment: Lean empowers employees to identify and address opportunities for improvement, and to take ownership of their work.
- Collaboration: Lean emphasizes collaboration and teamwork, both within and across functions, to deliver value to the customer.
- Customer Focus: Lean is customer-focused, and aims to deliver value to the customer by meeting their needs and exceeding their expectations.